
Lecture 00: Course Mechanics
DATA 503: Fundamentals of Data Engineering
January 12, 2026
About
Meet Your Professor
Dr. Lucas Cordova, Ph.D.
- Email: LPCordova@willamette.edu
Office Hours:
| Day | Time | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | 10:20 - 11:20 AM | Salem |
| Monday | 4:30 - 5:30 PM | Portland |
| Wednesday | 10:20 - 11:20 AM | Salem |
| Wednesday | 4:30 - 5:30 PM | Salem |
Teaching Assistant
TBD
- Email: TBD
- Office Hours: TBD
- Location: TBD
The TA will be available to help with:
- Assignment questions
- SQL debugging
- Project guidance
- General course support
Course Overview
What is Data Engineering?
Data Engineering is the practice of designing and building systems for collecting, storing, and analyzing data at scale.
Data engineers build the infrastructure that enables data scientists and analysts to do their work.
Why Data Engineering Matters
In the era of big data, organizations need professionals who can:
- Design scalable data architectures
- Build reliable data pipelines
- Ensure data quality and accessibility
- Bridge the gap between raw data and actionable insights
This course prepares you to be that professional.
Course Focus Areas
This course is split into two primary areas:
Relational Databases with SQL: Learning how to design, manage, and query relational databases using SQL with a focus on PostgreSQL
Data Engineering Pipelines: Understanding the components of the data engineering pipeline including data acquisition, transformation, and storage
You will gain both theoretical understanding and hands-on experience.
The Data Engineering Lifecycle
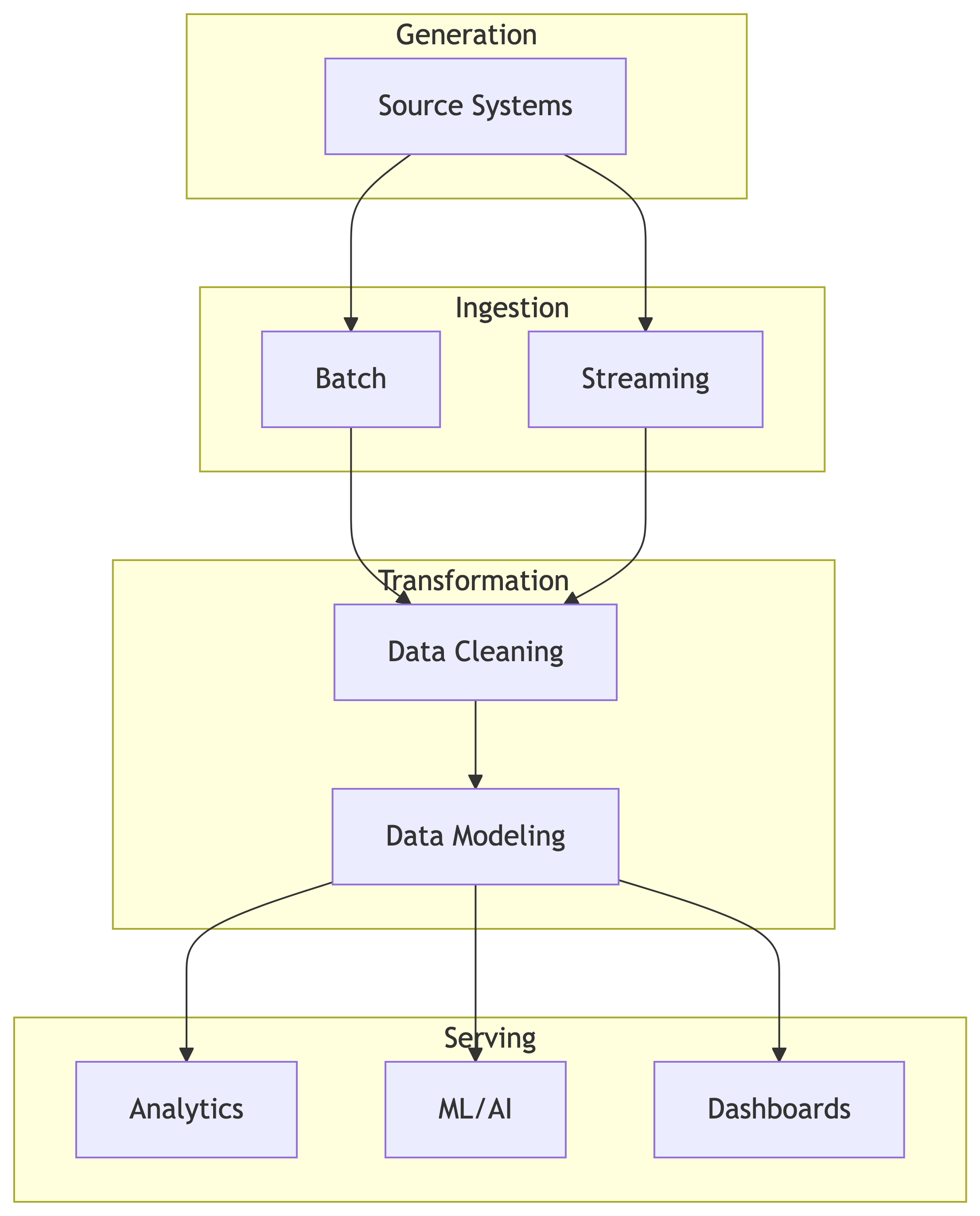
Course Learning Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this course, you will be able to:
- Understand the key tasks of a data engineer and their role in organizational pipelines
- Work with and query relational databases using SQL
- Analyze database design choices based on key factors
- Execute advanced SQL queries involving text mining and spatial data
- Explore alternatives to relational databases and current trends in data engineering
Learning Objectives
By the end of the course, you will be able to:
- Explain the purpose and advantages of relational databases
- Design and implement relational databases with tables and relationships
- Perform SQL queries, including advanced filters and joins
- Use SQL for text parsing and spatial data analysis
- Describe the role of data engineers in data pipelines
- Implement the full data engineering pipeline, from ingestion to serving data
Required Materials
Textbook (Required)
Practical SQL: A Beginner’s Guide to Storytelling with Data (2nd Edition)
- Author: Anthony DeBarros
- ISBN-13: 9781593278274
- Note: 1st Edition is acceptable, but chapters may differ
CodeGrade Enrollment Key (Required)
CodeGrade Enrollment Key ($35):
- Available via Bookstore (Bearcat Bundle) or personal credit card
- Accessed through Canvas (do not access CodeGrade directly)
- You will set up your account during the first assignment
Optional Textbooks
Fundamentals of Data Engineering
- Authors: Joe Reis and Matt Housley
- ISBN: 9781098108304
- A comprehensive overview of data engineering tasks and tools
The Data Warehouse Toolkit (3rd Edition)
- Authors: Ralph Kimball and Margy Ross
- ISBN-13: 978-1118530801
- A must-read for dimensional modeling and data warehouse design
Technology Requirements
Hardware:
- A laptop capable of running PostgreSQL
- Bring to class for hands-on activities
- Contact me if you need one provided
Software:
- PostgreSQL (latest stable version)
- Beekeeper Studio or pgAdmin
- Docker (later in semester)
- Text editor of your choice
Data Engineer’s Toolkit
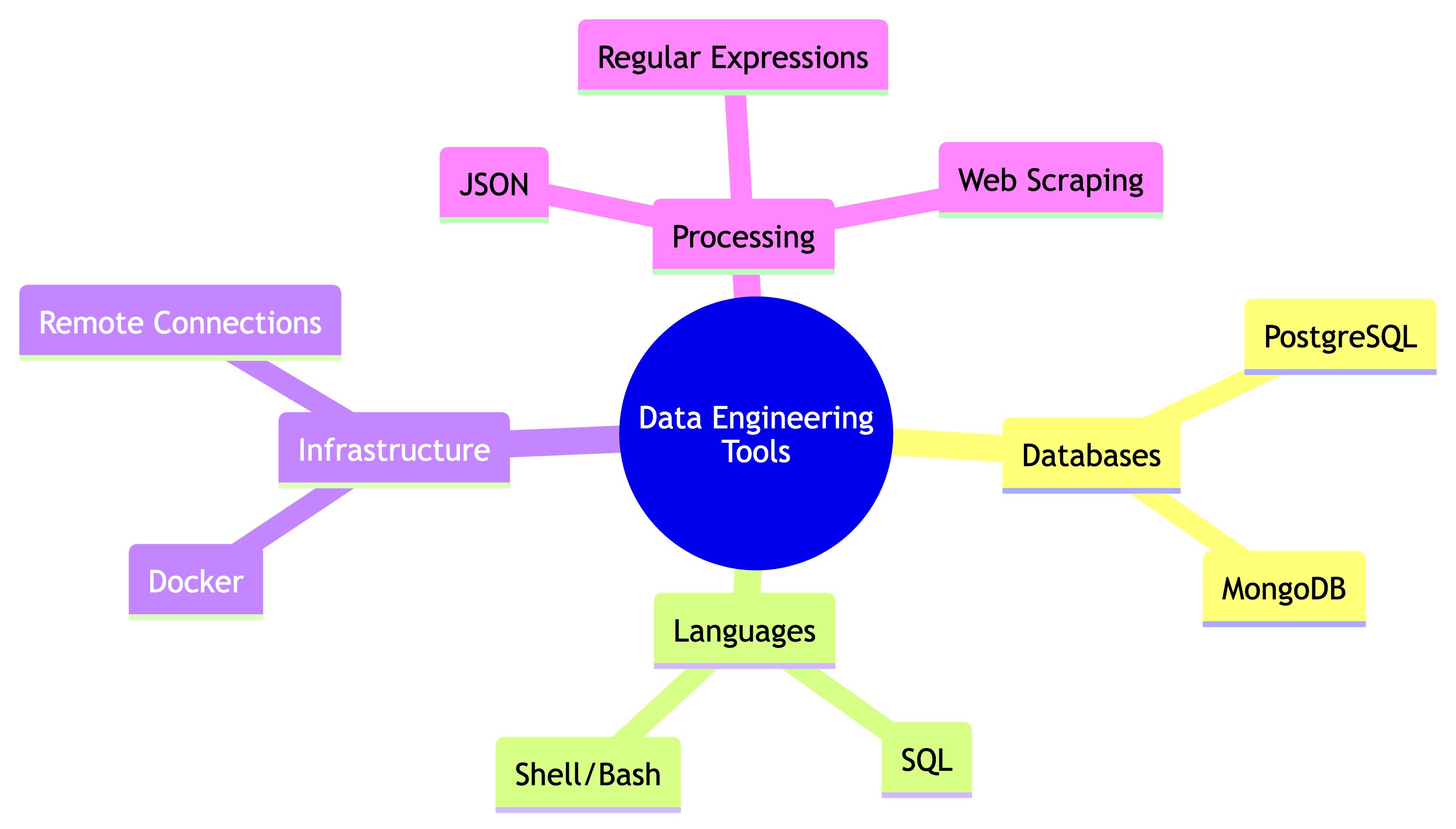
Assessments
Grade Breakdown
| Deliverable | Individual Weight | Total Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Attendance and Participation | ~1% each | 10% |
| Assignments (~10) | ~5% each | 50% |
| Midterm | 15% | 15% |
| Project | 30% | 25% |
| Total | 100% |
Letter Grade Distribution
| Grade | Range | Grade | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | >= 92.00 | C | 72.00 - 77.99 |
| A- | 90.00 - 91.99 | C- | 70.00 - 71.99 |
| B+ | 88.00 - 89.99 | D+ | 68.00 - 69.99 |
| B | 82.00 - 87.99 | D | 62.00 - 67.99 |
| B- | 80.00 - 81.99 | D- | 60.00 - 61.99 |
| C+ | 78.00 - 79.99 | F | <= 59.99 |
In-Class Exercises
Your grade for this category is based on:
- Attendance: Tracked randomly throughout the semester
- Active Participation: Completion of in-class exercises
Important notes:
- In-class exercises cannot be made up if missed
- These exercises are integral to your learning experience
- Come prepared and ready to contribute
Homework Assignments
Assignments reinforce concepts and techniques from lectures.
Each assignment challenges you to:
- Apply knowledge to solve specific problems
- Engage in design, coding, or analysis
- Work with real-world data engineering scenarios
Assignments are submitted via CodeGrade launched from Canvas.
Midterm Exam
The midterm is a video-based assessment.
Requirements:
- Create a 10 to 15 minute explanatory video
- Demonstrate understanding of course objectives
- Should be polished, similar to educational YouTube content
The due date and specific instructions will be communicated in advance. More to come on this! The midterm cannot be made up.
Project
A semester-long partner collaboration.
Project components:
- Partner work throughout the semester
- Graded milestones at key points
- Final deliverables include presentation, database structure, and analysis
- Presentations occur on the last day of class (Week 15)
Course Schedule
Semester Roadmap
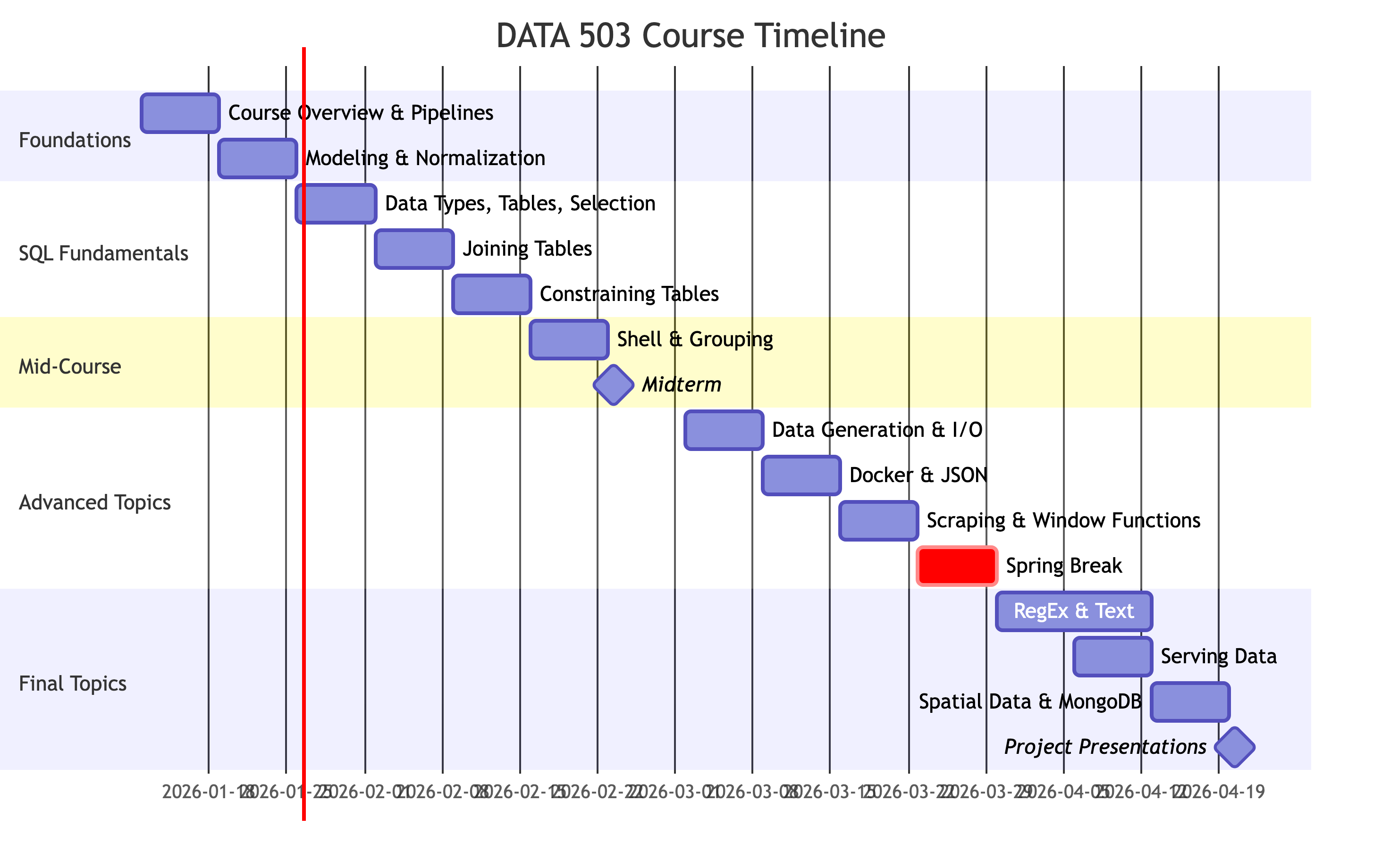
Weekly Schedule (Weeks 1-5)
| Week | Date | Topics | Due |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jan 12 | Course Overview, Data Engineering Pipelines | |
| 2 | Jan 19 | Modeling and Normalization, Environment Setup | Assignment 1 |
| 3 | Jan 26 | SQL: Data Types, I/O, Tables, Selection | Assignment 2 |
| 4 | Feb 2 | SQL: Joining Tables | Assignment 3 |
| 5 | Feb 9 | SQL: Constraining Tables | Assignment 4 |
Weekly Schedule (Weeks 6-10)
| Week | Date | Topics | Due |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Feb 16 | Shell, Remote Connections, Grouping | Project Proposal |
| 7 | Feb 23 | Midterm | Midterm |
| 8 | Mar 2 | SQL: Data Generation, I/O | Assignment 6, Project Forming |
| 9 | Mar 9 | Docker, JSON, SQL with JSON | Assignment 7 |
| 10 | Mar 16 | Web Scraping, Subqueries, Window Functions | Assignment 8 |
Weekly Schedule (Weeks 11-15)
| Week | Date | Topics | Due |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Mar 23 | Spring Break (No Class Mar 26) | |
| 12 | Mar 30 | Regular Expressions, Transforming Text | Project Milestone |
| 13 | Apr 6 | Dashboards, APIs, Views, Functions, Triggers | Assignment 10 |
| 14 | Apr 13 | Spatial Data (PostGIS), MongoDB | |
| 15 | Apr 20 | Project Presentations | Project, Presentation, Video |
Course Policies
Attendance Policy
Consistent attendance is essential for your success.
Expectations:
- Attend all classes and actively participate
- Come prepared and ready to contribute
- Attendance tracked explicitly or through participation activities
If you cannot attend due to illness or emergency, notify me as soon as possible.
Late Work Policy Overview
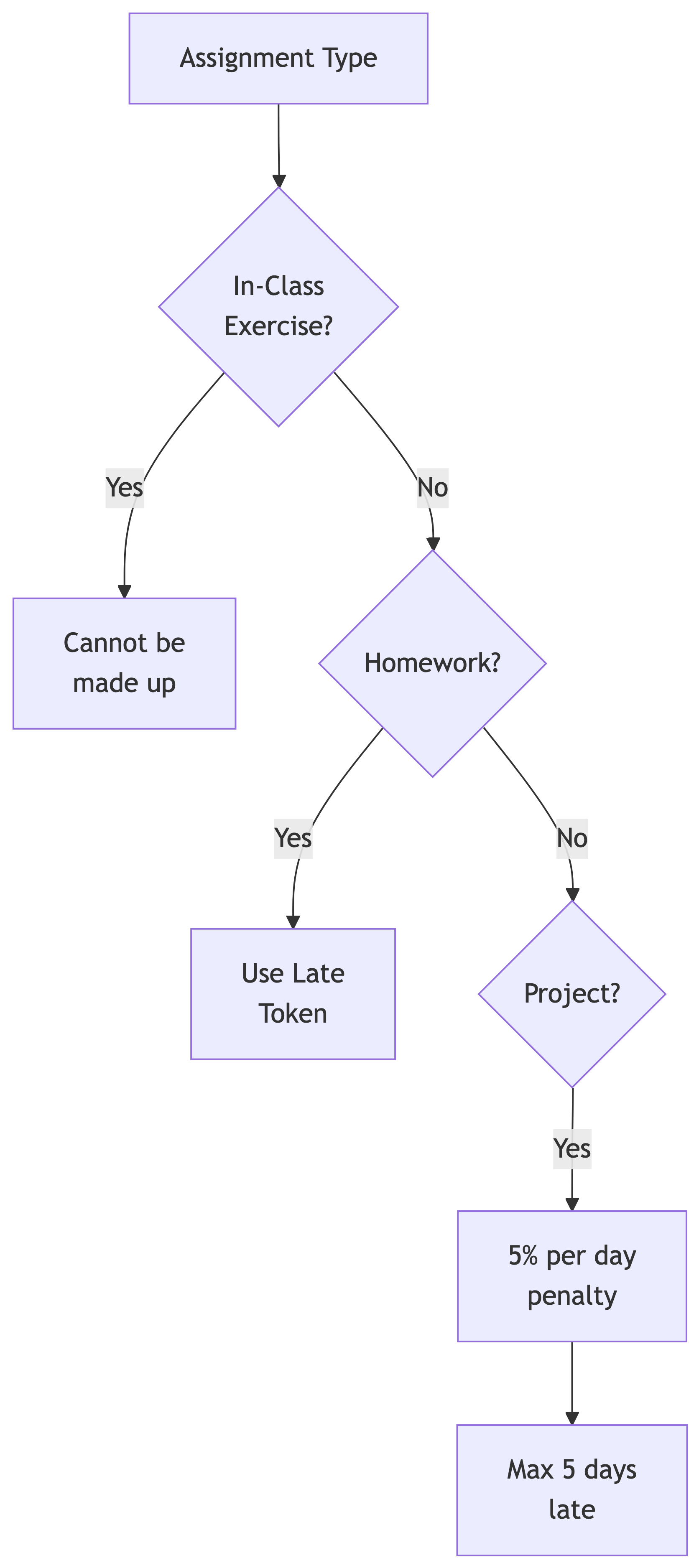
Late Tokens for Homework
Each student receives three late submission tokens at semester start.
How to use a token:
- Navigate to “Assignment Late Tokens” in Canvas
- Submit a text entry with the assignment number and expected completion date
- Wait for confirmation that the assignment has been reopened
Use tokens wisely. No additional tokens will be granted.
Project Late Policy
Late project submissions are accepted with penalties:
- 5% deduction per day late (including weekends and holidays)
- Submissions more than five days late will not be accepted
- Timely completion is critical for course progress
This policy encourages time management and accountability.
Incomplete Policy
An incomplete grade will only be granted for:
- Prolonged illness
- Family emergencies removing you from campus for extended periods
An incomplete will NOT be granted for:
- Falling behind due to lack of motivation
- Poor understanding of material
- Time management issues
If struggling, come see me! We can work out a plan.
Academic Integrity
General Statement
Cheating is defined as any form of intellectual dishonesty or misrepresentation.
Plagiarism consists of intentionally or unintentionally representing someone else’s work as your own.
Penalties range from grade reduction to failing the course.
Reasonable Actions
Things you CAN do:
- Discuss assignment requirements with classmates
- Brainstorm solution strategies verbally (no code sharing)
- Whiteboard solutions using diagrams or pseudocode
- Refer classmates to helpful resources
- Search the web for general concepts
- Use small code snippets from reliable sources (with citation)
- Work with a tutor (code must be your own)
Not Reasonable Actions
Things you CANNOT do:
- Submit another student’s work as your own
- Copy from another student’s quiz or exam
- View or copy another student’s code
- Copy solutions from previous years
- Ask for or buy solutions
- Share code in public forums
- Maintain public repositories of course solutions
Use of Generative AI
Reasonable Use:
- Generating ideas or examples
- Clarifying concepts
- Exploring potential solutions without copying verbatim
Not Reasonable Use:
- Copying AI-generated code directly
- Submitting AI-generated work as your own without significant personal input
When in doubt, ask!
University Policies
Inclusive Classroom Space
I will honor your affirmed name and pronouns.
- Initial information comes from SAGE
- Inform me if your affirmed name or pronouns differ
- Let me know if I make an error
Your feedback helps ensure I address you correctly.
Time Commitments
Willamette’s Credit Hour Policy:
For every hour of class time, expect 2-3 hours of work outside class.
For our 4-hour Monday session, anticipate 8-12 hours weekly of:
- Study time
- Reading and homework
- Assignments and research
- Group work
Diversity and Disability
Willamette values diversity and inclusion.
If aspects of this course create barriers to your inclusion or achievement, please notify me.
Accessible Education Services:
- Location: Matthews 103
- Phone: 503-370-6737
- Email: accessible-info@willamette.edu
SOAR Center
The Students Organizing for Access to Resources (SOAR) Center provides:
- Food (Bearcat Pantry)
- Toiletries
- Professional clothing
- Textbooks and scholarly resources
Location: Third floor of Putnam University Center
Contact: soar-center@willamette.edu
Getting Help
Resources Available
Office Hours:
- Drop-in or by appointment
- Multiple modalities (in-person, phone, Google Meet)
Teaching Assistant:
- TBD (details coming soon)
Email:
- LPCordova@willamette.edu
- Expect response within 24-48 hours
Tips for Success
- Attend class and participate actively
- Start assignments early to allow time for questions
- Practice SQL regularly outside of class
- Use office hours when stuck
- Collaborate appropriately with classmates
- Read the textbook alongside lectures
- Build your project incrementally at each milestone
Questions?
Let’s have a great semester learning Data Engineering!
Contact:
- Email: LPCordova@willamette.edu
- Office Hours: See schedule
Next Up:
Introduction to Data Engineering Pipelines