Lecture 03-1: SQL Joins
DATA 503: Fundamentals of Data Engineering
January 26, 2026
Joining Tables

Blockbuster Bend is the final video rental store. Today we connect data across the store’s database.
Blockbuster Bend Database
Load the Database
Run these commands to load the data into PostgreSQL:
ERD Overview
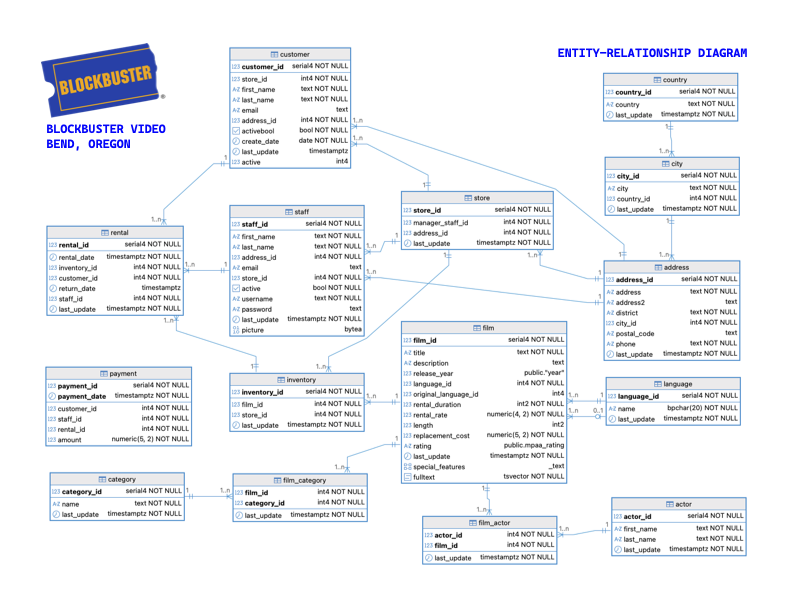
The ERD shows how tables connect through primary and foreign keys.
Crows-Foot Notation
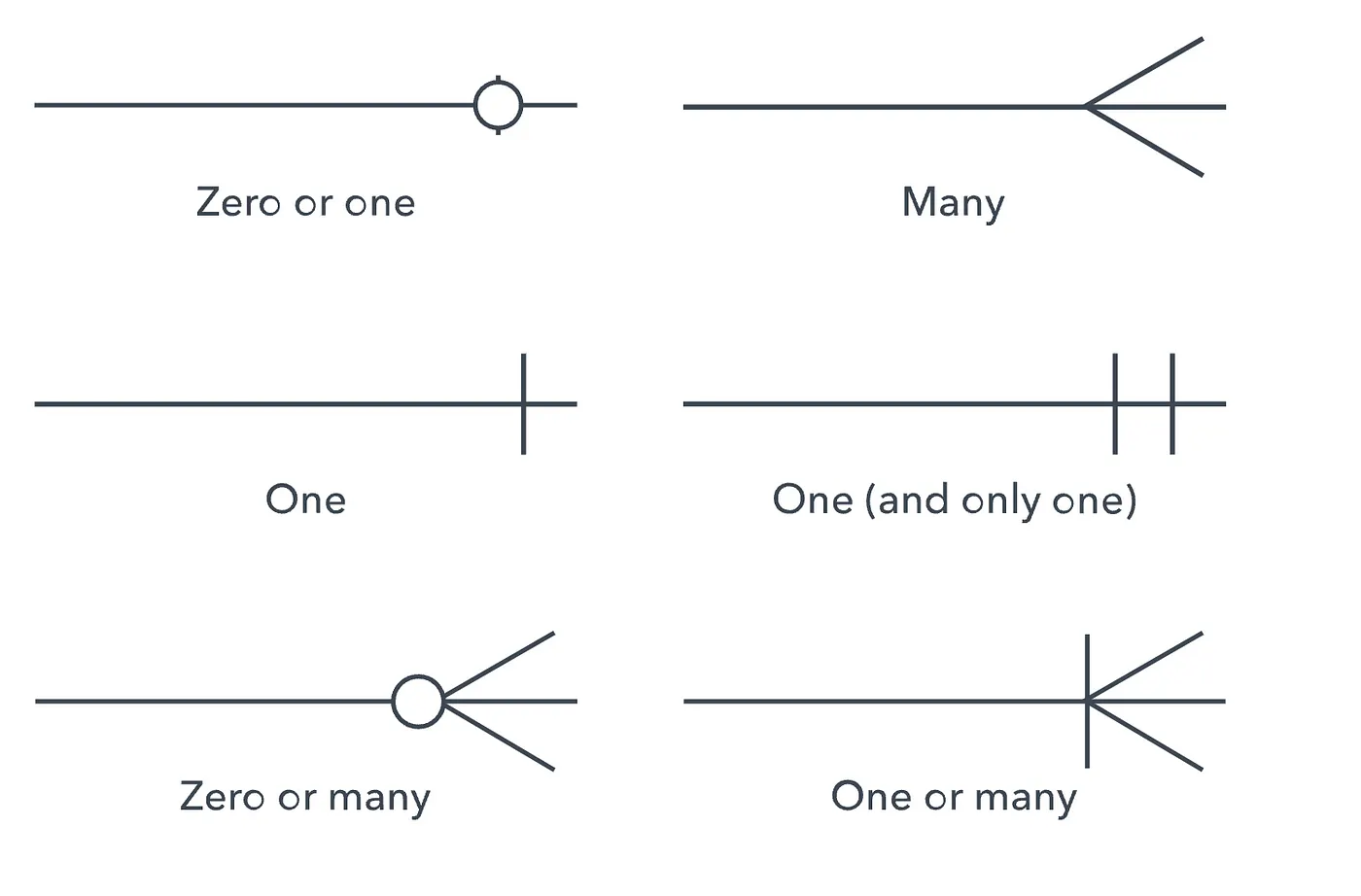
Crows-Foot Notation
Key Tables for Joins
The Blockbuster Bend database contains several interconnected table groups:
film- Movie titles and detailslanguage- Available languagescategory- Film genres (Action, Comedy, etc.)film_category- Links films to categories
actor- Actor namesfilm_actor- Links actors to filmscustomer- Customer informationstaff- Employee records
inventory- Physical copies of filmsrental- Rental transactionspayment- Payment records
store- Store locationsaddress- Street addressescity- City namescountry- Country names
Why Joins Matter
Business Questions Require Multiple Tables
Most real questions span multiple tables:
- Which films were rented last month and by whom?
- Which customers have never rented a film?
- Which categories generate the most revenue at each store?
- Which actors appear in Action films?
Joins let us answer these questions by connecting tables.
The Problem with Separate Tables
Consider these two tables from our database:
| film_id | title | language_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACADEMY DINOSAUR | 1 |
| 2 | ACE GOLDFINGER | 1 |
| 3 | ADAPTATION HOLES | 2 |
| language_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | English |
| 2 | Italian |
| 3 | Japanese |
| 4 | Mandarin |
| 5 | French |
| 6 | German |
How do we see film titles with their language names in a single result?
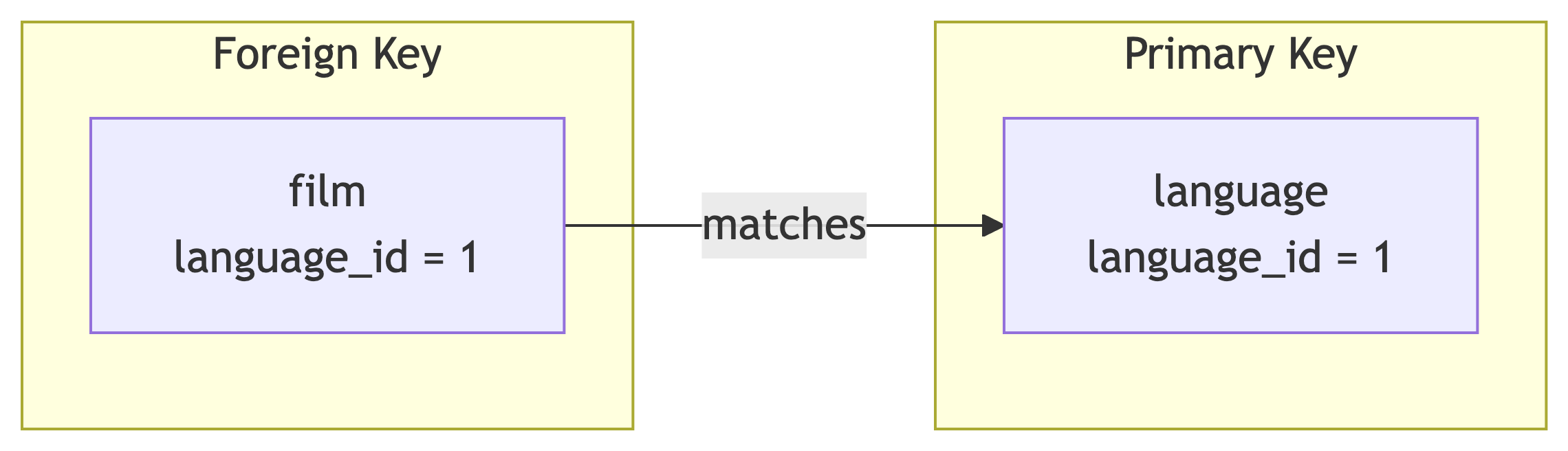
Keys Enable Joins
Primary Key: Uniquely identifies each row in a table (e.g., language_id in language)
Foreign Key: References a primary key in another table (e.g., language_id in film)
Inner Joins
Inner Join Concept
An inner join returns only rows where the join condition is satisfied in both tables.
Only matching rows are returned
- Films with a valid
language_id - Languages that have films assigned
- Unmatched rows are excluded
Inner Join with Sample Data
Let’s trace through an inner join step by step:
| film_id | title | language_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACADEMY DINOSAUR | 1 |
| 2 | ACE GOLDFINGER | 1 |
| 3 | ADAPTATION HOLES | 2 |
| 4 | AFFAIR PREJUDICE | 6 |
| 5 | AFRICAN EGG | 4 |
| language_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | English |
| 2 | Italian |
| 3 | Japanese |
| 4 | Mandarin |
| 5 | French |
| 6 | German |
The database compares each film’s language_id to the language table:
- ACADEMY DINOSAUR (language_id=1) matches English
- ACE GOLDFINGER (language_id=1) matches English
- ADAPTATION HOLES (language_id=2) matches Italian
- AFFAIR PREJUDICE (language_id=6) matches German
- AFRICAN EGG (language_id=4) matches Mandarin
| title | name |
|---|---|
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | English |
| ACE GOLDFINGER | English |
| ADAPTATION HOLES | Italian |
| AFFAIR PREJUDICE | German |
| AFRICAN EGG | Mandarin |
Note: Japanese and French have no films, so they do not appear.
SQL Query Structure
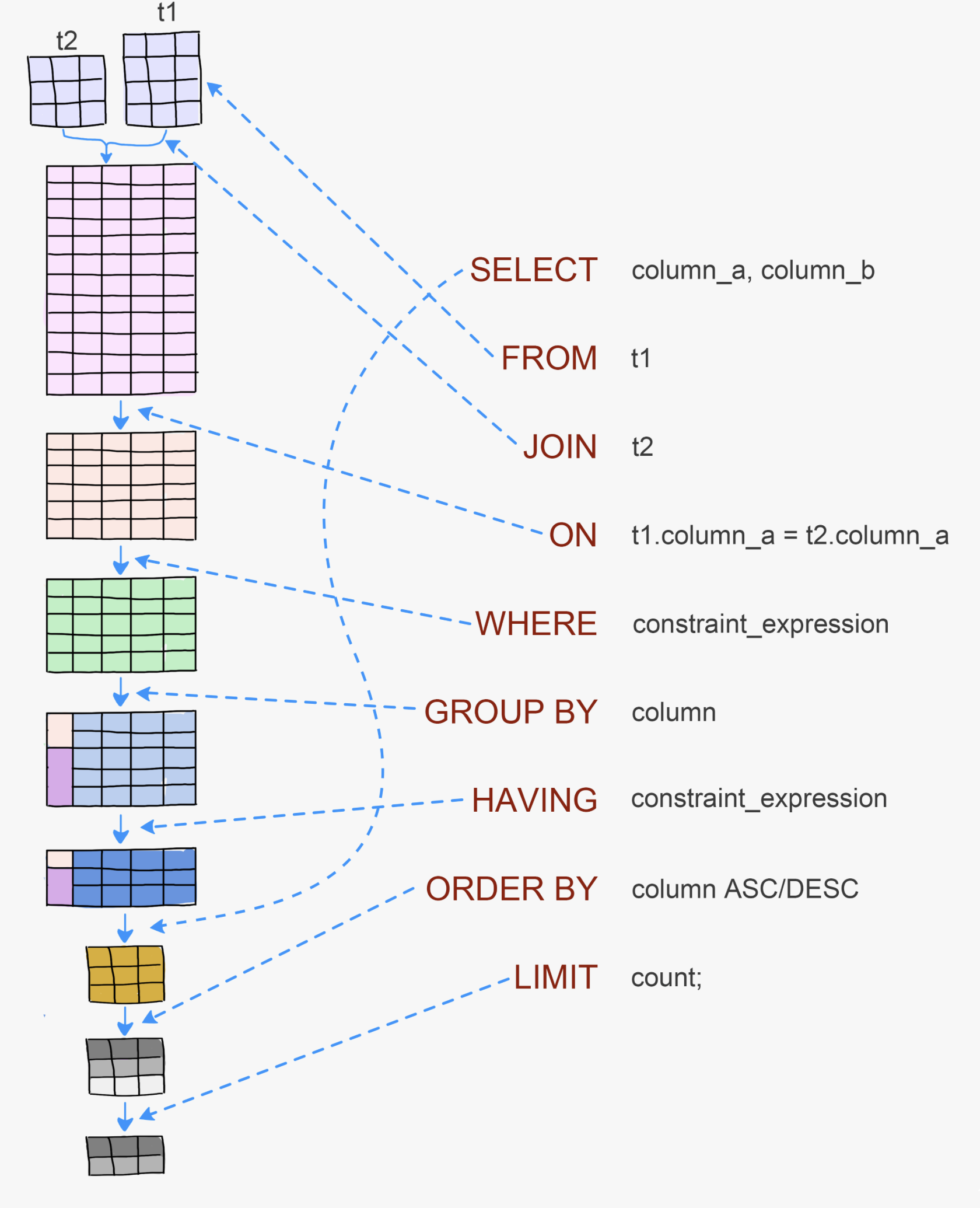
SQL Query Structure
Basic Inner Join Syntax
title | language
---------------------+----------
ACADEMY DINOSAUR | English
ACE GOLDFINGER | English
ADAPTATION HOLES | Italian
AFFAIR PREJUDICE | German
AFRICAN EGG | MandarinJOINis shorthand forINNER JOINAS fandAS lcreate table aliasesONspecifies the join condition- We can reference columns from both tables
Table Aliases Keep Joins Readable
Without aliases, queries become verbose and harder to read:
title | release_year | language
-------------------+--------------+----------
ACADEMY DINOSAUR | 2012 | English
AGENT TRUMAN | 2010 | English
ALASKA PHANTOM | 2016 | EnglishMulti-Table Joins: Film to Category
Films connect to categories through the film_category bridge table:

| title | category |
| ---------------- | -------- |
| ACE GOLDFINGER | Action |
| ADAPTATION HOLES | Action |
| AIRPLANE SIERRA | Action |
| ALASKA PHANTOM | Action |
| ANGELS LIFE | Action |- First join connects
filmtofilm_category - Second join connects
film_categorytocategory - The bridge table handles the many-to-many relationship
Film to Actor Join
The film_actor bridge table connects films and actors:
| title | first_name | last_name |
| ---------------- | ---------- | --------- |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | JOHNNY | CAGE |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | ROCK | DUKAKIS |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | CHRISTIAN | GABLE |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | PENELOPE | GUINESS |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | MARY | KEITEL |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | OPRAH | KILMER |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | WARREN | NOLTE |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | SANDRA | PECK |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | MENA | TEMPLE |
| ACADEMY DINOSAUR | LUCILLE | TRACY |
Practice: Customer Location Join
Write a query that returns:
customer_idfirst_namelast_namecity
Join customer to address to city. Order by last_name, then first_name. Limit to 5 rows.
| customer_id | first_name | last_name | city |
| ----------- | ---------- | --------- | ----------------------- |
| 505 | RAFAEL | ABNEY | Talavera |
| 504 | NATHANIEL | ADAM | Joliet |
| 36 | KATHLEEN | ADAMS | Arak |
| 96 | DIANA | ALEXANDER | Augusta-Richmond County |
| 470 | GORDON | ALLARD | Hodeida |Filtering: ON vs WHERE
Use ON for join conditions and WHERE for row filters:
| title | rating | category |
| ---------------- | ------ | -------- |
| ALI FOREVER | PG | Comedy |
| BLACKOUT PRIVATE | PG | Comedy |
| CAROL TEXAS | PG | Comedy |
| CHARADE DUFFEL | PG | Comedy |
| DISCIPLE MOTHER | PG | Comedy |ONdefines how tables relateWHEREfilters the joined result- Putting filters in
ONcan produce unexpected results with outer joins
Outer Joins
When Inner Joins Are Not Enough
Inner joins exclude rows without matches. Sometimes we need to see unmatched rows:
- Which languages have no films?
- Which customers have never rented?
- Which inventory items have never been rented?
Outer joins preserve unmatched rows.
Left Join Concept
A left join keeps all rows from the left table, even without matches.
All left table rows returned
- Matching rows show data from both tables
- Non-matching rows show
NULLfor right table columns
Left Join with Film and Inventory Data
Let’s say that we wish to list all films that we do not have a copy of in our inventory. In other words, we want to find all films that are not in the inventory table.
film (left table)
| film_id | title |
|---|---|
| 1 | ACADEMY DINOSAUR |
| 2 | ACE GOLDFINGER |
| 3 | ADAPTATION HOLES |
… (1000 rows)
inventory (right table)
| inventory_id | film_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
… (4581 rows)
| film_id | title | inventory_id |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | ALICE FANTASIA | NULL |
| 33 | APOLLO TEEN | NULL |
| 36 | ARGONAUTS TOWN | NULL |
| 38 | ARK RIDGEMONT | NULL |
… (42 rows)
LEFT JOINkeeps all films- Films without a matching inventory get
NULLvalues WHERE i.inventory_id IS NULLfilters to only unmatched rows
Right Join Concept
A right join keeps all rows from the right table, even without matches.
All right table rows returned
- Equivalent to a left join with tables swapped
- Less common in practice
Full Outer Join Concept
A full outer join keeps all rows from both tables.
All rows from both tables
- Unmatched left rows show NULL for right columns
- Unmatched right rows show NULL for left columns
- Useful for finding all mismatches
What Would Left Join and Right Join Look Like for these Tables?
Table A
| id | value_a |
|---|---|
| 1 | Apple |
| 2 | Banana |
| 3 | Cherry |
Table B
| id | value_b |
|---|---|
| 2 | Two |
| 3 | Three |
| 4 | Four |
Full Outer Join Example
Table A
| id | value_a |
|---|---|
| 1 | Apple |
| 2 | Banana |
| 3 | Cherry |
Table B
| id | value_b |
|---|---|
| 2 | Two |
| 3 | Three |
| 4 | Four |
| a.id | value_a | b.id | value_b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple | NULL | NULL |
| 2 | Banana | 2 | Two |
| 3 | Cherry | 3 | Three |
| NULL | NULL | 4 | Four |
Outer Join Comparison Summary
| Join Type | Left Table | Right Table | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| INNER JOIN | Only matched | Only matched | Standard queries |
| LEFT JOIN | All rows | Only matched | Find unmatched in right |
| RIGHT JOIN | Only matched | All rows | Find unmatched in left |
| FULL OUTER JOIN | All rows | All rows | Find all unmatched |
Practice: Unrented Inventory
Find inventory items that have never been rented.
Return:
inventory_idfilm_idtitlestore_id
Order by store_id, then inventory_id. Limit to 5 rows.
inventory_id | film_id | title | store_id
-------------+---------+-------------------+----------
1 | 1 | ACADEMY DINOSAUR | 1
2 | 1 | ACADEMY DINOSAUR | 1
...Cross Joins
Cross Join Concept
A cross join (Cartesian product) returns every combination of rows from both tables.
No join condition
- Every row in A pairs with every row in B
- Result size = rows(A) x rows(B)
- Can produce very large results
Cross Join with Sample Data
store
| store_id |
|---|
| 1 |
| 2 |
category (partial)
| category_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Action |
| 5 | Comedy |
| 7 | Drama |
| store_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Action |
| 1 | Comedy |
| 1 | Drama |
| 2 | Action |
| 2 | Comedy |
| 2 | Drama |
Every store paired with every category (2 x 3 = 6 rows).
Cross Join Use Case: Store-Category Grid
Generate a planning grid for all store-category combinations:
store_id | category | planned_inventory
---------+------------+------------------
1 | Action | 0
1 | Animation | 0
1 | Children | 0
1 | Classics | 0
1 | Comedy | 0
1 | Documentary| 0
1 | Drama | 0
1 | Family | 0
1 | Foreign | 0
1 | Games | 0- Inventory planning templates
- Report scaffolding
- Generating test data
- Date/category combinations for analysis
Cross Join Caution
Cross joins can create enormous result sets:
| Table A Rows | Table B Rows | Result Rows |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 100 | 10,000 |
| 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,000,000 |
| 10,000 | 10,000 | 100,000,000 |
Always use WHERE or LIMIT when exploring cross joins.
Self Joins
Self Join Concept
A self join joins a table to itself. This is useful when:
- Comparing rows within the same table
- Finding hierarchical relationships
- Detecting duplicates or related records
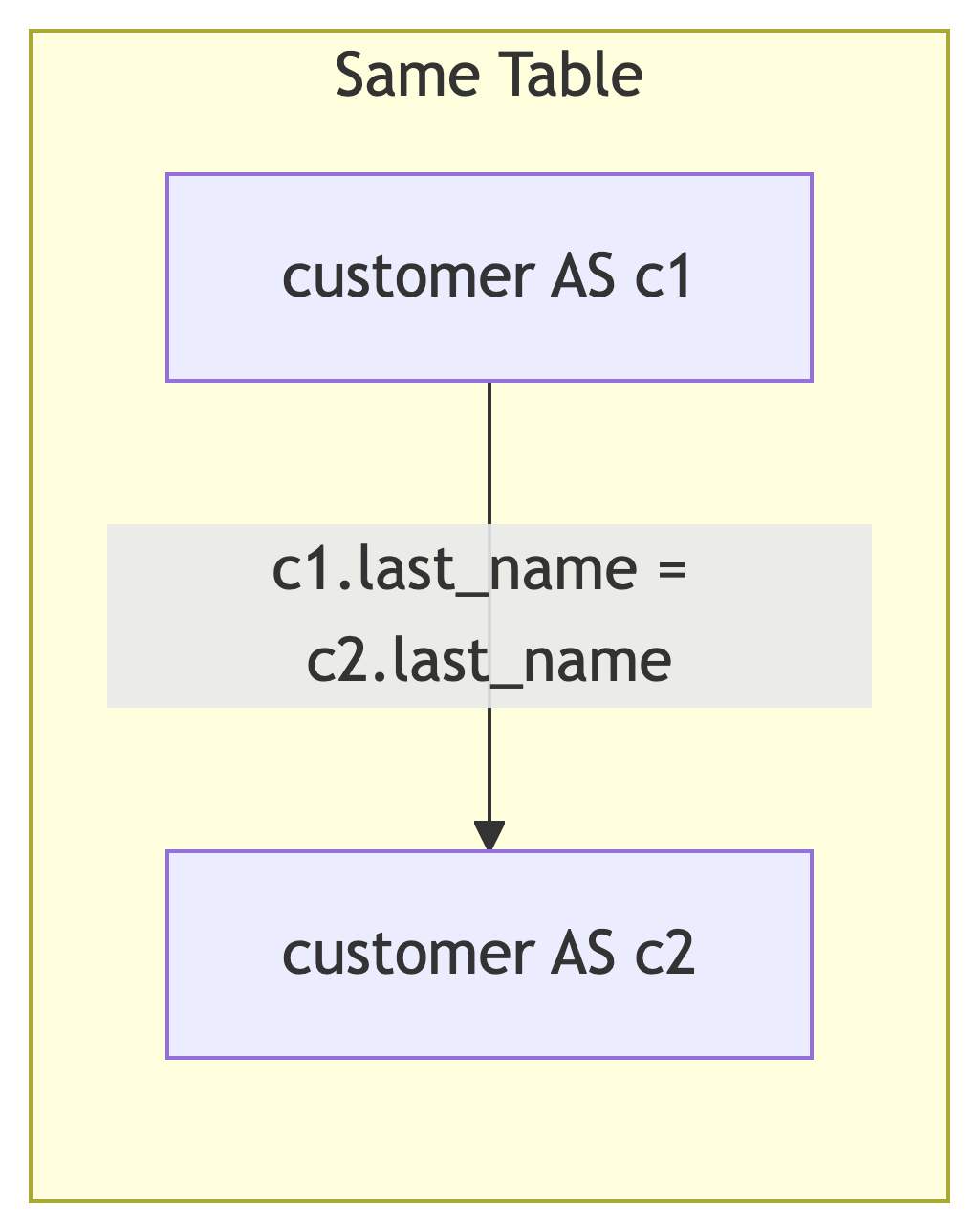
Finding Customers with Same Last Name
customer_1 | first_1 | last_name | customer_2 | first_2
-----------+-----------+-----------+------------+---------
318 | BRIAN | WYMAN | 412 | JOHN
...- Table aliased as both
c1andc2 c1.customer_id < c2.customer_idprevents duplicate pairs- Without this condition, we would get (A,B) and (B,A)
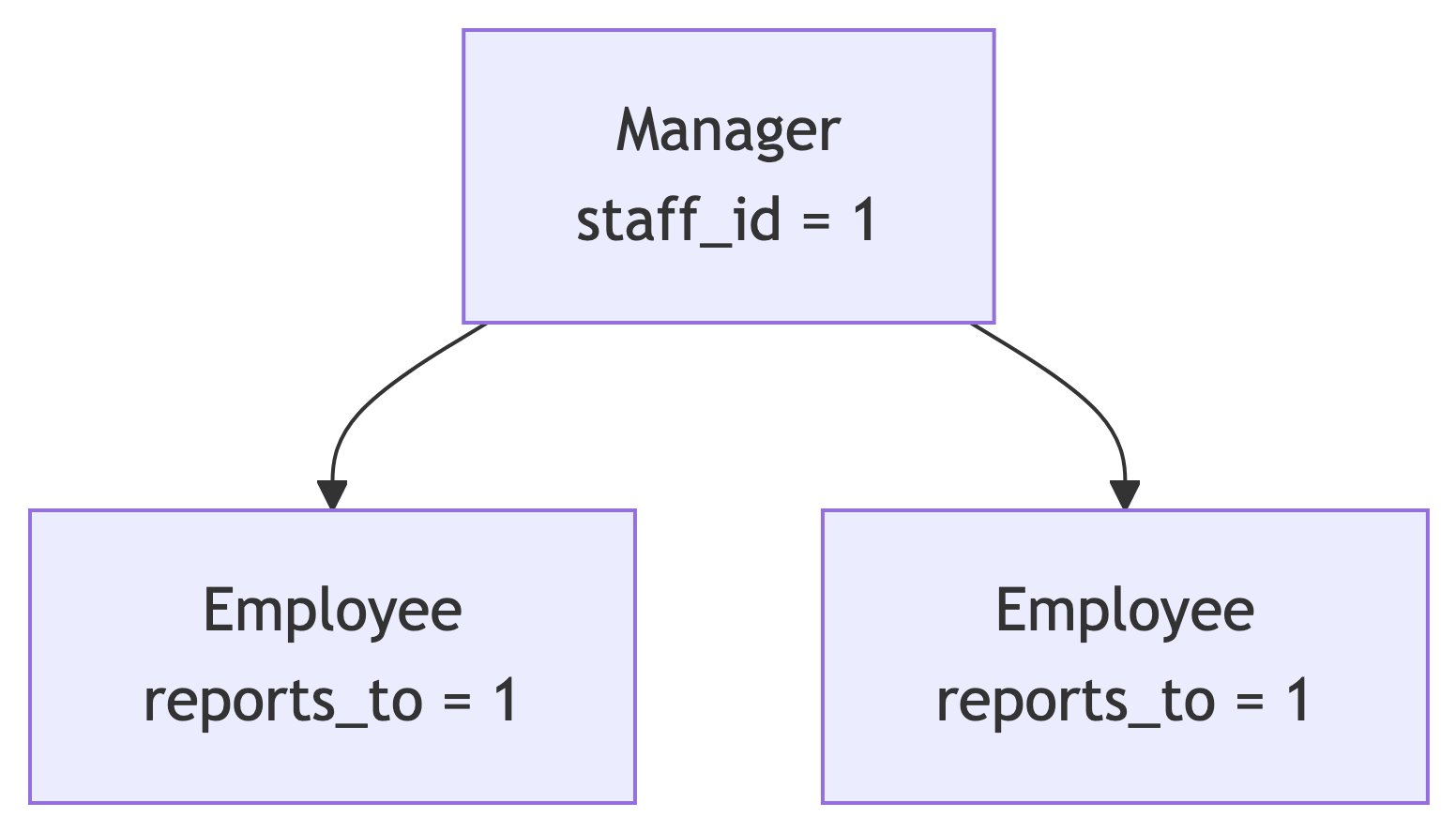
Self Join for Hierarchical Data
Self joins work well for parent-child relationships:
Multi-Table Join Patterns
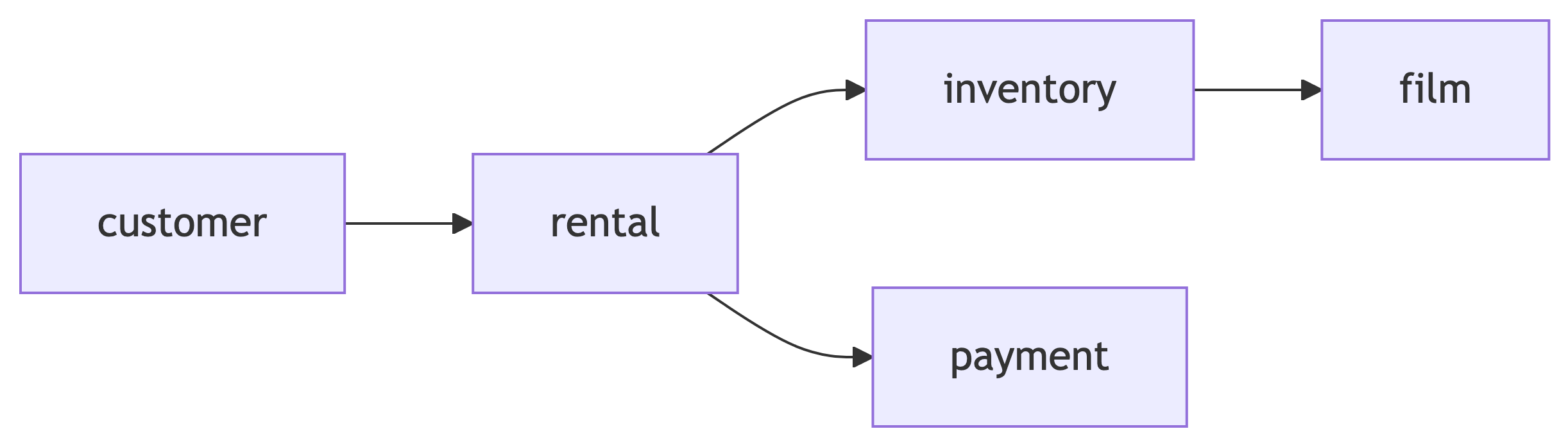
The Rental Transaction Chain
Tracking a rental requires joining multiple tables:
Complete Rental Query
SELECT
c.first_name || ' ' || c.last_name AS customer,
f.title,
r.rental_date::date AS rented,
r.return_date::date AS returned,
p.amount
FROM customer AS c
JOIN rental AS r
ON c.customer_id = r.customer_id
JOIN inventory AS i
ON r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
JOIN film AS f
ON i.film_id = f.film_id
JOIN payment AS p
ON r.rental_id = p.rental_id
ORDER BY r.rental_date DESC
LIMIT 5;customer | title | rented | returned | amount
------------------+--------------------+------------+------------+-------
AUSTIN CINTRON | SOMETHING DUCK | 2022-07-27 | 2022-08-02 | 4.99
AUSTIN CINTRON | TITANS JERK | 2022-07-27 | 2022-08-01 | 4.99
AUSTIN CINTRON | SUNRISE LEAGUE | 2022-07-27 | 2022-07-28 | 2.99
...customertorentalviacustomer_idrentaltoinventoryviainventory_idinventorytofilmviafilm_idrentaltopaymentviarental_id
Actor Filmography Query
SELECT
a.first_name,
a.last_name,
f.title,
f.release_year,
c.name AS category
FROM actor AS a
JOIN film_actor AS fa
ON a.actor_id = fa.actor_id
JOIN film AS f
ON fa.film_id = f.film_id
JOIN film_category AS fc
ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
JOIN category AS c
ON fc.category_id = c.category_id
WHERE a.last_name = 'GUINESS'
ORDER BY f.release_year, f.title;first_name | last_name | title | release_year | category
-----------+-----------+--------------------+--------------+----------
PENELOPE | GUINESS | ACADEMY DINOSAUR | 2012 | Documentary
PENELOPE | GUINESS | ANACONDA CONFESSIONS| 2020 | Animation
...Five tables joined through their foreign key relationships.
Join on Multiple Columns
Sometimes joins need multiple columns to match correctly:
payment_id | customer_id | rental_id | amount | rental_date
-----------+-------------+-----------+--------+------------
17503 | 1 | 76 | 2.99 | 2022-05-25
17504 | 1 | 573 | 0.99 | 2022-05-28
17505 | 1 | 1185 | 5.99 | 2022-06-15
...- Composite keys
- Data validation
- Ensuring correct matches in denormalized data
Common Pitfalls
Ambiguous Column Names
When two tables have the same column name:
ERROR: column reference "customer_id" is ambiguousMissing Join Conditions
Forgetting the ON clause creates a cross join:
Every film paired with every category (1000 x 16 = 16,000 rows).
Cartesian Explosion
Adding more tables can multiply result sizes:
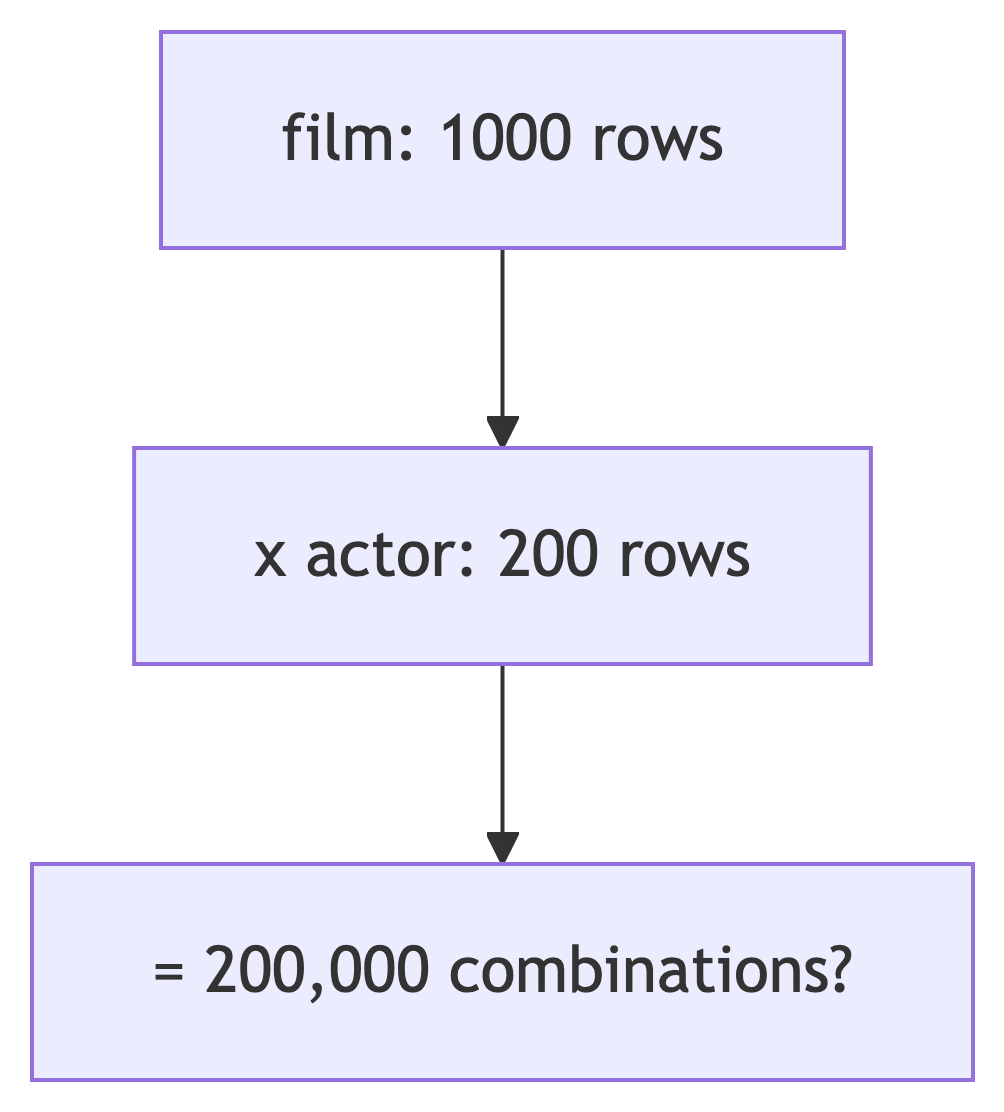
Prevention:
- Check join conditions carefully
- Use
COUNT(*)beforeSELECT * - Add
LIMITduring development
Join Verification Checklist
Before running a complex join:
- Are all join conditions specified?
- Are column references qualified with aliases?
- Is this an inner or outer join?
- Could any join create a Cartesian product?
- Have I tested with
LIMITfirst?
Practice Problems
Practice 1: Store Revenue by Category
For each store, find total revenue by film category.
Return:
store_idcategorytotal_revenue
Order by store_id, then total_revenue descending.
SELECT
i.store_id,
c.name AS category,
SUM(p.amount) AS total_revenue
FROM payment AS p
JOIN rental AS r ON p.rental_id = r.rental_id
JOIN inventory AS i ON r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
JOIN film AS f ON i.film_id = f.film_id
JOIN film_category AS fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
JOIN category AS c ON fc.category_id = c.category_id
GROUP BY i.store_id, c.name
ORDER BY i.store_id, total_revenue DESC;store_id | category | total_revenue
---------+-------------+--------------
1 | Sports | 4892.19
1 | Sci-Fi | 4756.98
1 | Animation | 4656.30
...Practice 2: Actors Without Films
Find any actors who have no films in the database.
Return:
actor_idfirst_namelast_name
Order by last_name, first_name.
actor_id | first_name | last_name
---------+------------+----------
(0 rows - all actors have films in this database)Practice 3: Customer Rental History
Create a rental history for customer MARY SMITH (customer_id = 1).
Return:
rental_datetitlecategoryamount
Order by rental_date descending. Limit to 10 rows.
SELECT
r.rental_date::date,
f.title,
c.name AS category,
p.amount
FROM customer AS cu
JOIN rental AS r ON cu.customer_id = r.customer_id
JOIN payment AS p ON r.rental_id = p.rental_id
JOIN inventory AS i ON r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
JOIN film AS f ON i.film_id = f.film_id
JOIN film_category AS fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
JOIN category AS c ON fc.category_id = c.category_id
WHERE cu.customer_id = 1
ORDER BY r.rental_date DESC
LIMIT 10;Key Takeaways
Join Type Summary
| Join Type | Returns | NULL Handling |
|---|---|---|
| INNER JOIN | Only matching rows | No NULLs from join |
| LEFT JOIN | All left + matched right | NULLs for unmatched right |
| RIGHT JOIN | All right + matched left | NULLs for unmatched left |
| FULL OUTER JOIN | All rows from both | NULLs for unmatched on both sides |
| CROSS JOIN | All combinations | No join condition |
| SELF JOIN | Table joined to itself | Depends on join type used |
Best Practices
- Always use table aliases for readability
- Qualify all column references to avoid ambiguity
- Use explicit JOIN syntax instead of comma-separated tables
- Put join conditions in ON, filters in WHERE
- Test with LIMIT before running full queries
- Verify row counts to catch Cartesian products
Exit Ticket
Write a query that answers:
Which films were rented in 2022 by customers from store 1?
Return the customer name, film title, and rental date.
Be ready to share your join path and key columns.
References
References
- Forta, B. (2024). SQL in 10 Minutes a Day (6th ed.). Addison-Wesley.
- PostgreSQL Documentation. SELECT - Joins. https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/queries-table-expressions.html
- Silberschatz, A., Korth, H., & Sudarshan, S. (2019). Database System Concepts (7th ed.). McGraw-Hill.